
Hexagram 5 of the Yi Jing is composed of the upper trigram ☵ 坎 Kan (Water, the younger, water element) and the lower trigram ☰ 乾 Qian (Heaven, the father).
Interpretation from comments: Confident waiting, the moment when one measures the danger with the assurance of overcoming it.
In Chinese: 水天需 Shuǐ Tiān Xū, the English translation is “Waiting.”
Jia Zi combination of the hexagram: Hexagram 5 of the I Ching is associated with the Yi Si 乙巳 combination of the sexagesimal cycle, the 42nd combination in the cycle:
- 乙 Yi, celestial stem Wood Yin.
- 巳 Si, terrestrial branch of the Serpent.
Interpretation of the drawing of hexagram 5 of the I Ching
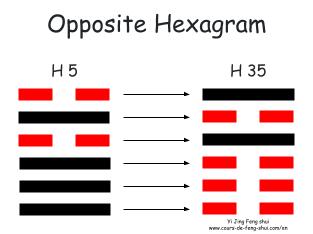
Opposite hexagram (錯卦 Cuo Gua): The opposite hexagram indicates everything that is not or the opposite of the solution to the situation.
The opposite hexagram is obtained by replacing the Yang lines with Yin lines and vice versa, resulting in Hexagram 35 – Jin (Progress).
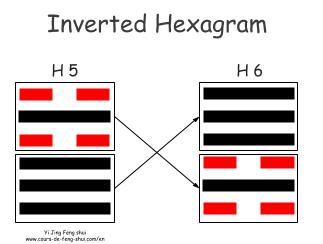
Inverted Hexagram (覆卦 Fu Gua): The permuted hexagram provides information on the origin of the situation.
The permuted hexagram is obtained by swapping the two trigrams, resulting in Hexagram 6 – Song (Conflict).
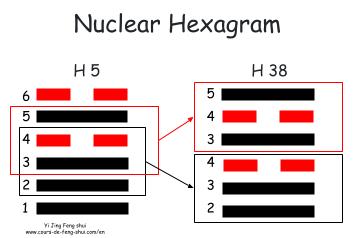
Nuclear (Mutual) Hexagram (互卦 Hu Gua): The nuclear hexagram represents the core of the problem or question.
The nuclear hexagram is obtained by using the four central lines to form two trigrams, resulting in Hexagram 38 – Kui (Opposition).
Mutant Hexagram (derived): The mutation of a line results in a new hexagram, which indicates the evolution of the situation.
- Line 6 mutates: the resulting hexagram is H9.
- Line 5 mutates: the resulting hexagram is H11.
- Line 4 mutates: the resulting hexagram is H43.
- Line 3 mutates: the resulting hexagram is H60.
- Line 2 mutates: the resulting hexagram is H63.
- Line 1 mutates: the resulting hexagram is H48.
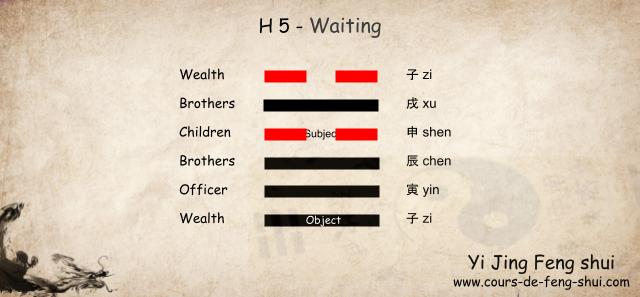
Taoist Yi Jing – Wen Wang Gua
Characteristics of hexagram 5 for the Taoist interpretation of the Yi Jing using the Wen Wang Gua (Liu yao) divination method:
Hexagram 5 is a wandering hexagram (of change) from the Kun (Earth) family. In this hexagram, the Subject is placed on the fourth line, and the Object is placed on the first line.
The Six Relatives:
- 6th line: 子 Zi (Water) – Wealth
- 5th line: 戌 Xu (Earth) – Brothers
- 4th line: 申 Shen (Metal) – Children
- 3rd line: 辰 Chen (Earth) – Brothers
- 2nd line: 寅 Yin (Wood) – Officer
- 1st line: 子 Zi (Water) – Wealth